Now Reading: The Silent Threat: Asymptomatic Colon Cancer and Diagnostic Challenges
-
01
The Silent Threat: Asymptomatic Colon Cancer and Diagnostic Challenges
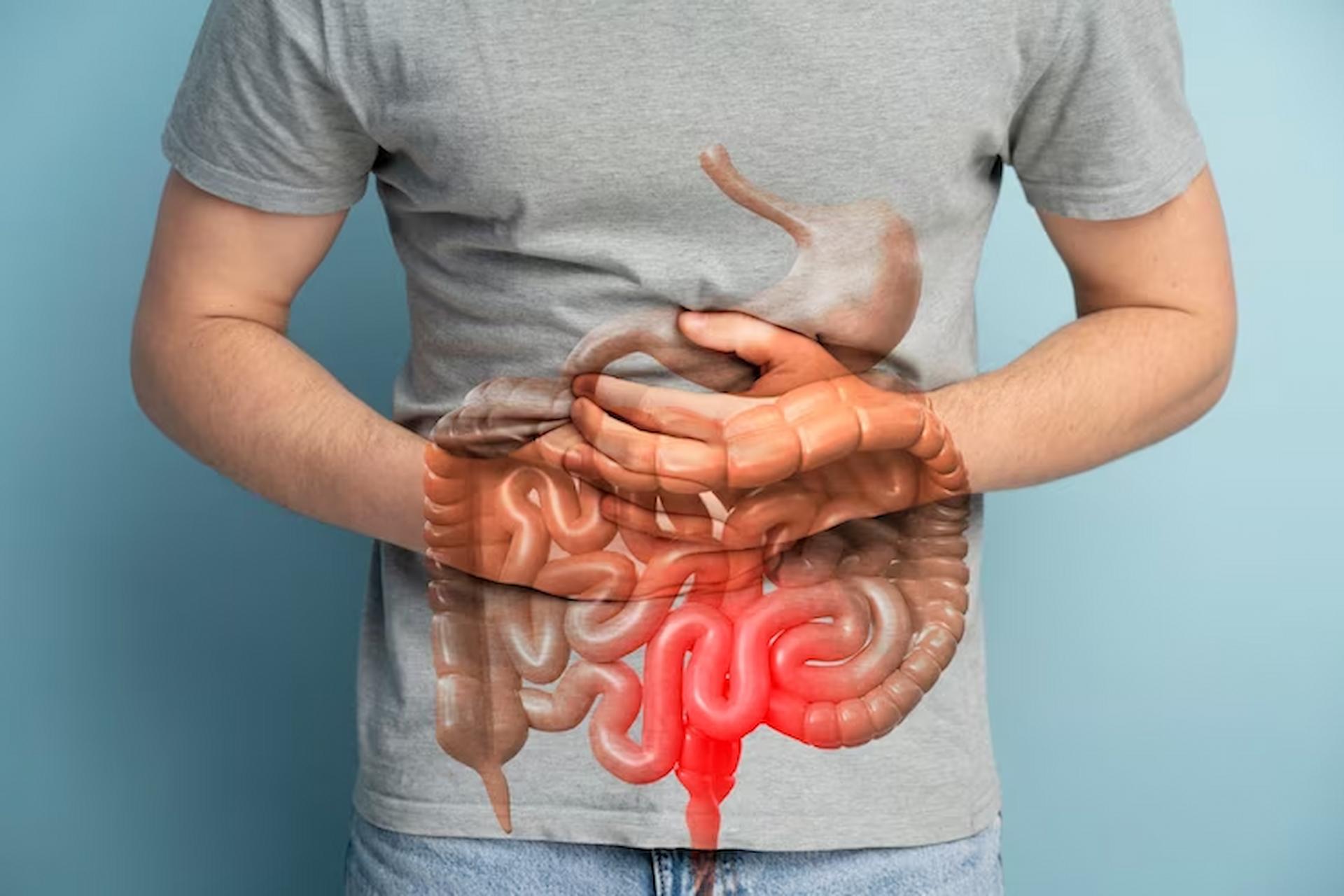
The Silent Threat: Asymptomatic Colon Cancer and Diagnostic Challenges
Colon cancer, a formidable adversary in the realm of cancer, often presents diagnostic challenges when it manifests without evident symptoms. Asymptomatic colon cancer, also known as silent or occult colon cancer, poses a unique set of difficulties in early detection and can significantly impact patient outcomes.
In this article, we delve into the complexities surrounding asymptomatic colon cancer, shedding light on the diagnostic challenges and the importance of proactive screening.
Understanding Asymptomatic Colon Cancer
Colon cancer typically exhibits symptoms in its later stages, making early detection crucial for successful treatment. However, in some cases, individuals with colon cancer may remain asymptomatic, meaning they experience no noticeable signs or symptoms even as the cancer develops.
Colon Cancer Symptoms: The Elusive Clues
Absence of Obvious Warning Signs
Asymptomatic colon cancer is characterized by the absence of obvious warning signs commonly associated with the disease. Unlike symptomatic cases where individuals may experience changes in bowel habits, rectal bleeding, or abdominal discomfort, those with asymptomatic colon cancer may remain unaware of the growing threat within their digestive system.
Challenges in Early Detection
The lack of overt symptoms complicates the early detection of asymptomatic colon cancer. Routine screenings, such as colonoscopies, play a pivotal role in identifying precancerous polyps or early-stage cancer. However, without apparent colon cancer symptoms prompting individuals to seek medical attention, the urgency for preventive screenings may be diminished.
Diagnostic Challenges in Asymptomatic Cases
Delayed Diagnosis and Advanced Stages
Asymptomatic colon cancer often goes undetected until it reaches advanced stages. Without noticeable symptoms to prompt medical evaluation, individuals may delay seeking screening or medical advice, allowing the cancer to progress unchecked. By the time the cancer is diagnosed, it may have advanced to a more challenging and less treatable stage.
Risk Factors and Screening Recommendations
Identifying individuals at risk for colon cancer is essential for implementing proactive screening measures. Age, family history, and certain lifestyle factors contribute to the risk of developing colon cancer. However, without apparent symptoms, individuals may overlook or underestimate their risk, further delaying necessary screenings.
Proactive Screening and Prevention
Colonoscopies: A Gold Standard in Prevention
Colonoscopies remain a gold standard in preventing and detecting colon cancer. Despite the challenges posed by asymptomatic cases, routine screenings become imperative, especially for individuals with risk factors such as age or family history. Colonoscopies can identify and remove precancerous polyps before they develop into cancer.
Raising Awareness: The Role of Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers play a crucial role in raising awareness about the importance of screenings and preventive measures, even in the absence of apparent colon cancer symptoms. Encouraging discussions about risk factors, family history, and the potential benefits of routine screenings can motivate individuals to prioritize their digestive health.
Public Health Campaigns
Public health campaigns dedicated to colon cancer awareness and prevention can significantly impact early detection rates. Educating the public about the potential risks, the importance of screenings, and the role of a healthy lifestyle can empower individuals to take proactive steps toward preventing colon cancer.
Navigating a Path to Early Detection
Individual Responsibility
While healthcare providers and public health initiatives play pivotal roles, individuals must take responsibility for their health. Being proactive about understanding personal risk factors, staying informed about preventive measures, and advocating for routine screenings can contribute to early detection and improved outcomes.
Advancements in Screening Technologies
Ongoing advancements in screening technologies offer promise in addressing the challenges posed by asymptomatic colon cancer. Non-invasive screening options, such as fecal immunochemical tests (FIT) or virtual colonoscopies, provide alternatives for individuals who may be hesitant to undergo traditional colonoscopies.
Conclusion
Asymptomatic colon cancer poses a silent threat that demands heightened awareness and proactive measures for early detection. The absence of apparent colon cancer symptoms underscores the need for routine screenings, especially in individuals with risk factors. Healthcare providers, public health campaigns, and individual responsibility collectively form a formidable alliance in navigating the diagnostic challenges posed by asymptomatic cases.