Now Reading: Types of Treatments for People with Dementia
-
01
Types of Treatments for People with Dementia

Types of Treatments for People with Dementia
Dementia presents a formidable challenge, impacting millions globally, with Alzheimer’s disease standing out as the most prevalent form. While a cure remains elusive, there are several treatments available to manage symptoms and enhance quality of life. Understanding the types of treatments available is crucial for caregivers and families supporting loved ones with dementia.
Medications
In addition to cholinesterase inhibitors and memantine, other medications may be prescribed based on the specific symptoms and progression of dementia. Antipsychotic medications, for example, may be used to manage behavioral symptoms such as aggression or hallucinations.
However, these medications are typically used with caution due to their potential side effects, especially in older adults. It’s important for healthcare providers to regularly review medication regimens to ensure they are appropriate and effective. Non-drug approaches, such as music therapy or aromatherapy, may also be considered complementary treatments to help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
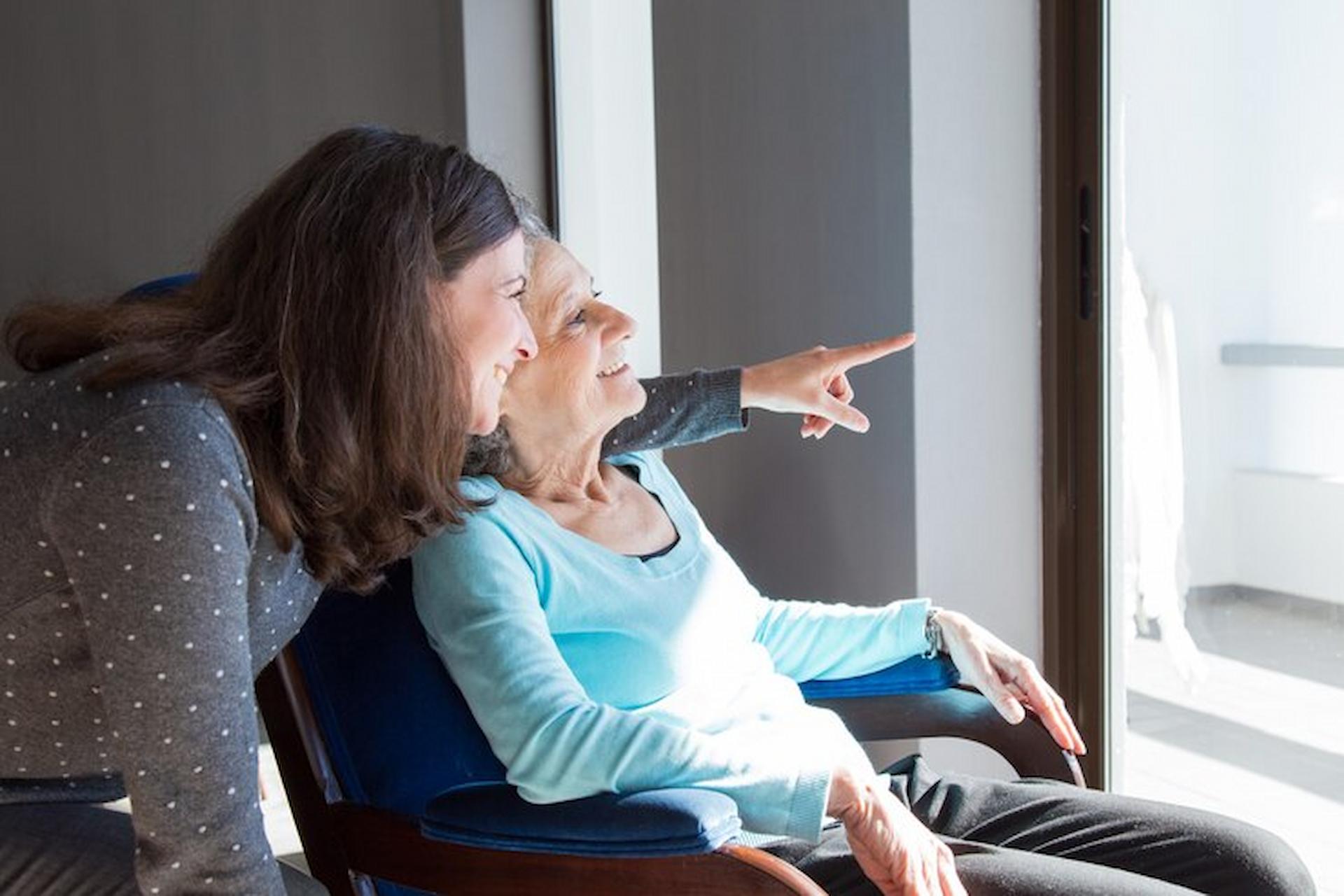
Support Services
Dementia-friendly communities can provide a supportive environment where individuals with dementia can engage in activities and socialize without feeling stigmatized. Respite care services provide caregivers with a temporary break from their caregiving duties, ensuring their loved ones receive high-quality care in the meantime.
Moreover, support groups can link caregivers with individuals encountering similar challenges, fostering a sense of community and empathy. Care homes also play a vital role in delivering support by offering a secure and pleasant setting for those with dementia. For example, morriscare.co.uk offers specialized dementia care services, including personalized care plans and dementia-friendly facilities, to support residents and their families.
Psychological Therapies
In addition to CST and reminiscence therapy, other psychological approaches like cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) can be advantageous for individuals with dementia. CBT aims to modify negative thought patterns and behaviors, potentially enhancing mood and coping mechanisms.
Additionally, supportive counseling can provide emotional support and strategies for managing the challenges of living with dementia. These therapies can be tailored to the individual’s needs and preferences, enhancing their effectiveness and overall well-being.
Occupational Therapy
Occupational therapists may also recommend assistive devices such as walkers or specialized communication devices to help individuals with dementia maintain independence. They can also provide education and support to family members and caregivers, helping them understand how best to support their loved ones with dementia. Additionally, occupational therapy can help individuals with dementia engage in meaningful activities that promote cognitive function and social interaction. By focusing on abilities rather than disabilities, occupational therapy can improve quality of life and overall well-being.
Physical Exercise
Including a range of physical activities like walking, dancing, or yoga can offer both physical and mental advantages for individuals with dementia. Exercise can enhance cardiovascular health, muscle strength, and balance, lowering the risk of falls. It can also enhance mood and cognition, promoting overall well-being. Caregivers and family members can encourage regular physical activity by participating in activities with their loved ones, making it a fun and social experience. Additionally, exercise programs specifically designed for individuals with dementia can provide structure and motivation, helping them stay active and engaged.